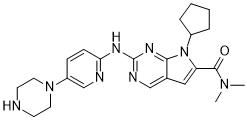
Ribociclib
CAS#: 1211441-98-3
Description: Ribociclib, also known as LEE011, is a n orally available cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor targeting cyclin D1/CDK4 and cyclin D3/CDK6 cell cycle pathway, with potential antineoplastic activity. CDK4/6 inhibitor LEE011 specifically inhibits CDK4 and 6, thereby inhibiting retinoblastoma (Rb) protein phosphorylation. Inhibition of Rb phosphorylation prevents CDK-mediated G1-S phase transition, thereby arresting the cell cycle in the G1 phase, suppressing DNA synthesis and inhibiting cancer cell growth. Overexpression of CDK4/6, as seen in certain types of cancer, causes cell cycle deregulation. Check for active clinical trials or closed clinical trials using this agent. (NCI Thesaurus).
Synonym: LEE011; LEE-011. LEE 011; Ribociclib.
IUPAC/Chemical Name: 7-cyclopentyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-((5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
THEORETICAL ANALYSIS
Name: Ribociclib (LEE011)
CAS#: 1211441-98-3
Chemical Formula: C23H30N8O
Exact Mass: 434.25426
Molecular Weight: 434.54
Elemental Analysis: C, 63.57; H, 6.96; N, 25.79; O, 3.68
TECHNICAL DATA
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Related CAS#
1211441-98-3 (Ribociclib free base)
1211443-80-9 (Ribociclib hydrochloride)
1374639-75-4 (Ribociclib succinate)
REFERENCES
1: Burki TK. Ribociclib in HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2016 Oct 13. pii: S1470-2045(16)30502-2. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30502-2. PubMed PMID: 27746106.
2: Hart LS, Rader J, Raman P, Batra V, Russell MR, Tsang M, Gagliardi M, Chen L, Martinez D, Li Y, Wood A, Kim S, Parasuraman S, Delach S, Cole KA, Krupa S, Boehm M, Peters M, Caponigro G, Maris JM. Preclinical therapeutic synergy of MEK1/2 and CDK4/6 inhibition in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 11. pii: clincanres.1131.2016. PubMed PMID: 27729458.
3: Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, Campone M, Blackwell KL, André F, Winer EP, Janni W, Verma S, Conte P, Arteaga CL, Cameron DA, Petrakova K, Hart LL, Villanueva C, Chan A, Jakobsen E, Nusch A, Burdaeva O, Grischke EM, Alba E, Wist E, Marschner N, Favret AM, Yardley D, Bachelot T, Tseng LM, Blau S, Xuan F, Souami F, Miller M, Germa C, Hirawat S, O’Shaughnessy J. Ribociclib as First-Line Therapy for HR-Positive, Advanced Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016 Oct 7. PubMed PMID: 27717303.
4: Martinello R, Genta S, Galizia D, Geuna E, Milani A, Zucchini G, Valabrega G, Montemurro F. New and developing chemical pharmacotherapy for treating hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016 Sep 27:1-11. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 27646965.
5: Infante JR, Cassier PA, Gerecitano JF, Witteveen PO, Chugh R, Ribrag V, Chakraborty A, Matano A, Dobson JR, Crystal AS, Parasuraman S, Shapiro GI. A Phase I Study of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib (LEE011) in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors and Lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Aug 19. pii: clincanres.1248.2016. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed PMID: 27542767.
6: Chen P, Lee NV, Hu W, Xu M, Ferre RA, Lam H, Bergqvist S, Solowiej J, Diehl W, He YA, Yu X, Nagata A, VanArsdale T, Murray BW. Spectrum and Degree of CDK Drug Interactions Predicts Clinical Performance. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Oct;15(10):2273-2281. PubMed PMID: 27496135.
7: Barroso-Sousa R, Shapiro GI, Tolaney SM. Clinical Development of the CDK4/6 Inhibitors Ribociclib and Abemaciclib in Breast Cancer. Breast Care (Basel). 2016 Jun;11(3):167-73. doi: 10.1159/000447284. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Review. PubMed PMID: 27493615; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4960359.
8: Gampenrieder SP, Rinnerthaler G, Greil R. CDK4/6 inhibition in luminal breast cancer. Memo. 2016;9:76-81. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Review. PubMed PMID: 27429659; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4923084.
9: Curigliano G, Gómez Pardo P, Meric-Bernstam F, Conte P, Lolkema MP, Beck JT, Bardia A, Martínez García M, Penault-Llorca F, Dhuria S, Tang Z, Solovieff N, Miller M, Di Tomaso E, Hurvitz SA. Ribociclib plus letrozole in early breast cancer: A presurgical, window-of-opportunity study. Breast. 2016 Aug;28:191-8. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jun 20. PubMed PMID: 27336726.
10: O’Sullivan CC. CDK4/6 inhibitors for the treatment of advanced hormone receptor positive breast cancer and beyond: 2016 update. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;17(12):1657-67. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2016.1201072. Epub 2016 Jun 27. PubMed PMID: 27322766.
11: Kim HK, Kim SY, Lee SJ, Kang M, Kim ST, Jang J, Rath O, Schueler J, Lee DW, Park WY, Kim SJ, Park SH, Lee J. BEZ235 (PIK3/mTOR inhibitor) Overcomes Pazopanib Resistance in Patient-Derived Refractory Soft Tissue Sarcoma Cells. Transl Oncol. 2016 Jun;9(3):197-202. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2016.03.008. Epub 2016 May 12. PubMed PMID: 27267837; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4907899.
12: Okano M, Ohtake T, Saji S. [Combination Therapy of Molecular-Targeted Drugs for Breast Cancer — Their Potential in the Future]. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2016 Apr;43(4):398-403. Japanese. PubMed PMID: 27220784.
13: DiPippo AJ, Patel NK, Barnett CM. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Breast Cancer: Past, Present, and Future. Pharmacotherapy. 2016 Jun;36(6):652-67. doi: 10.1002/phar.1756. Epub 2016 May 28. Review. PubMed PMID: 27087139.
14: O’Leary B, Finn RS, Turner NC. Treating cancer with selective CDK4/6 inhibitors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016 Jul;13(7):417-30. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.26. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Review. PubMed PMID: 27030077.
15: Hamilton E, Infante JR. Targeting CDK4/6 in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Apr;45:129-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Review. PubMed PMID: 27017286.
16: Roskoski R Jr. Cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitors including palbociclib as anticancer drugs. Pharmacol Res. 2016 May;107:249-75. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Review. PubMed PMID: 26995305.
17: Spring L, Bardia A, Modi S. Targeting the cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6-retinoblastoma pathway with selective CDK 4/6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: rationale, current status, and future directions. Discov Med. 2016 Jan;21(113):65-74. PubMed PMID: 26896604.
18: Perez EA. Treatment strategies for advanced hormone receptor-positive and human epidermal growth factor 2-negative breast cancer: the role of treatment order. Drug Resist Updat. 2016 Jan;24:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 10. PubMed PMID: 26830312.
19: O’Sullivan CC. Overcoming Endocrine Resistance in Hormone-Receptor Positive Advanced Breast Cancer-The Emerging Role of CDK4/6 Inhibitors. Int J Cancer Clin Res. 2015;2(4). pii: 029. Epub 2015 Oct 14. PubMed PMID: 26726315; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4697745.
20: Steger GG, Gnant M, Bartsch R. Palbociclib for the treatment of postmenopausal breast cancer – an update. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17(2):255-63. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2016.1133590. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Review. PubMed PMID: 26679057.